What is the working principle of pelletizing machine?
Introduction
Pelletizing machines are widely used in various industries to convert raw materials into small, cylindrical pellets. These pellets are in high demand for fuel, animal and fish feed, fertilizers, and many other applications. The working principle of a pelletizing machine is essential to understand, as it determines the efficiency and quality of the pellet production process. In this article, we will delve into the intricate details of the working principle of a pelletizing machine, exploring each step involved in the pelletization process.
The Importance of Pelletizing
Before diving into the working principle, it is crucial to understand the significance of pelletizing. The pelletization process serves to transform loose, fine, or heterogeneous raw materials into homogeneous, dense, and durable pellets. The benefits of pelletizing include improved handling, transportation, and storage, as well as enhanced material properties such as increased bulk density, reduced moisture content, and better chemical characteristics.
Raw Material Preparation
The pelletizing process starts with raw material preparation. The first step involves acquiring suitable raw materials, which can vary depending on the desired pellet product. Common raw materials used in pelletizing include wood chips, sawdust, agricultural residues, animal feed, and various biomass materials. These raw materials undergo a series of processes such as sorting, grinding, and drying to achieve the desired characteristics.
During the sorting phase, impurities such as stones, metals, or foreign objects are removed to ensure product quality. Subsequently, the raw materials are ground into finer particles to facilitate the pelletizing process. Grinding can be achieved through various methods, including hammer mills, grinders, or crushers. Additionally, if the raw material has high moisture content, it needs to be dried before further processing. Proper drying is essential to eliminate excess moisture and ensure optimal pelletization.
Forcing the Material through the Die
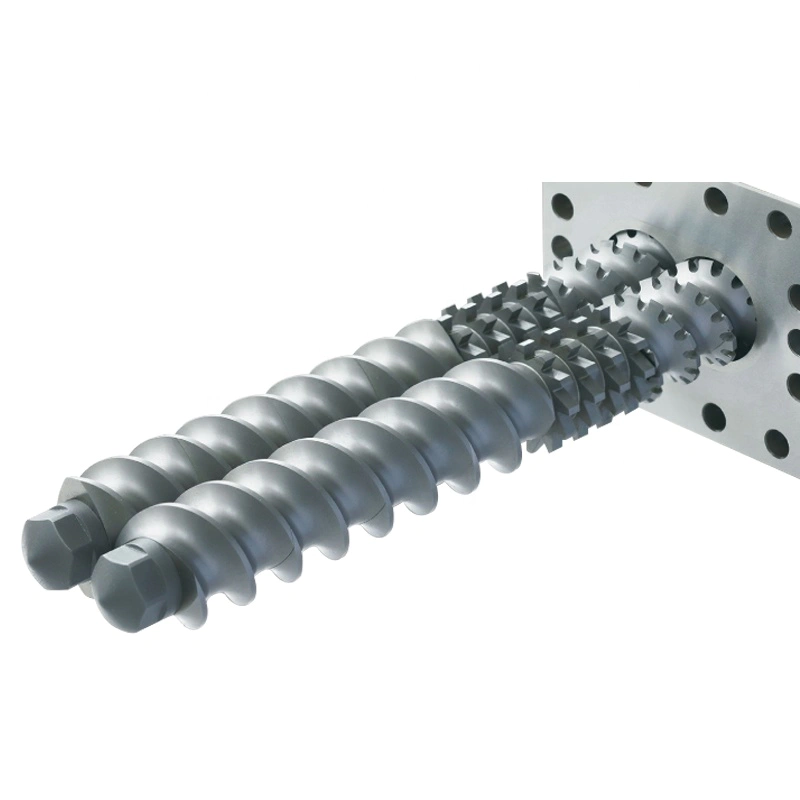
Once the raw materials are prepared, they are fed into the pelletizing machine for compaction. The pelletizing machine consists of a die, rollers, and a feed hopper. The die is a metal plate with small holes through which the raw material will be forced to form pellets. The rollers, mounted on top of the die, apply pressure on the raw material to push it through the die holes.
The process of forcing the material through the die requires careful consideration of variables such as temperature, pressure, and the composition of the raw material. These parameters influence the pelletization process and the quality of the resulting pellets. The pressure exerted by the rollers compresses the raw material and creates heat due to friction. This heat softens the lignin in the raw material, acting as a natural binder to hold the pellets together.
Role of the Die in Pellet Formation
The die plays a crucial role in shaping the pellets. It has small holes with diameters ranging from a few millimeters to a few centimeters, depending on the desired pellet size. The holes in the die impart the cylindrical shape to the pellets as the raw material is extruded through them. The design of the die can vary, including flat dies or ring dies, depending on the specific application and the type of pelletizing machine.
The die also assists in controlling the density and hardness of the pellets. By altering the size and arrangement of the die holes, it is possible to produce pellets with different characteristics. For instance, reducing the hole diameter will increase the density and hardness of the pellets, making them suitable for applications that require durability, such as fuel pellets. On the other hand, larger holes result in lighter and less dense pellets, which are preferred for applications like animal feed.
Cooling and Sizing the Pellets
After the pellets are extruded through the die, they are still hot and soft. Therefore, to maintain their desired shape and durability, they need to be appropriately cooled and sized. The cooling process involves passing the freshly formed pellets through a cooling chamber, where cool air or water is circulated. This rapid cooling solidifies the pellets, making them harder and easier to handle.
Once cooled, the pellets are then sieved or screened to achieve uniform size distribution. Unevenly sized pellets can cause issues during storage, transport, and usage. Therefore, achieving the required pellet size is crucial for maintaining product consistency. Pellets that are too large are typically crushed or ground to the desired size, while fines or undersized pellets are usually recycled or used for other purposes.
Pellet Quality Assurance
Quality assurance is a vital aspect of pellet production, ensuring that the pellets meet the required standards and specifications. Various parameters are evaluated to assess the quality of pellets, including density, durability, moisture content, ash content, and calorific value. Density determines the weight and volume of the pellets, while durability reflects their resistance to breakage during handling and usage.
Moisture content plays a crucial role in the longevity and stability of the pellets. If the moisture content is too high, it can lead to mold growth, degradation, or clumping of the pellets. Conversely, excessively low moisture content can result in pellet brittleness and reduced durability. Ash content is another important factor, representing the inorganic components present in the pellets, such as minerals or impurities.
Summary
In summary, the working principle of a pelletizing machine involves several steps, from raw material preparation to the production of high-quality pellets. The initial stage includes sorting, grinding, and drying the raw materials to achieve the desired characteristics. Subsequently, the prepared raw materials are forced through a die by rollers, forming cylindrical pellets.
The die plays a crucial role in shaping the pellets and controlling their density and hardness. After extrusion, the pellets undergo cooling and sizing processes to ensure their durability and uniformity. Additionally, quality assurance measures are implemented to assess pellet attributes such as density, durability, moisture content, ash content, and calorific value.
Understanding the working principle of a pelletizing machine is essential for industries that rely on pellet production for their products. By optimizing each step of the pelletization process, manufacturers can achieve efficient and consistent pellet production, meeting the requirements of various applications like fuel, animal and fish feed, fertilizers, and more.